Force majeure in construction
The term ‘force majeure’ comes from French law, where it translates as 'superior force' (as opposed to ‘vis majeure’ or ‘vis major’ which refers to an act of God). Whilst in France, the term has a defined legal meaning, in English law it does not, and it is dealt with in different ways by different forms of contract.
Very broadly, it relates to exceptional, unforeseen events or circumstances that are beyond the reasonable control of a party to a contract and which prevent or impede performance of their obligations under the contract. Generally it cannot be an event that the party could reasonably have avoided or overcome, or an event attributable to the other party.
Clauses referring to force majeure attempt to set out the circumstances to which the term applies to and prescribe how such situations should be treated. Depending on the provisions of the contract, the following may be considered to constitute force majeure:
- Unforeseen changes to legislation.
- Wars and other hostilities (such as terrorism).
- Fires.
- Exceptionally adverse weather.
- Civil unrest, such as riots or revolution.
- Strikes (other than by the contractor or subcontractors).
- Natural catastrophes such as earthquakes, floods and volcanoes.
- Epidemics or pandemics.
In some contracts, force majuere is considered a 'relevant event', that may allow the contractor to claim an extension of time if they have been prevented or impeded from performing their obligations under the contract. Although, if the contractor has continued to perform their duties, despite the occurrence, they may not be able to make a claim.
As these conditions tend not to be defined, it can be difficult to determine whether they have arisen or not. For example, when does a virulent virus constitute an epidemic? This has become particularly significant in recent years due to the increasing number of exceptionally adverse weather events (in particular flooding), as well events such as foot and mouth, swine flu and restrictions on air travel due to volcanic ash clouds.
Whilst clients will generally accept the contractor cannot perform their duties under the contract where there is genuine force majeure, problems arise when the client believes the contractor is unnecessarily claiming force majeure for commercial gain and that the situation could have been foreseen, avoided or mitigated. Disputed claims are particularly common in relation to exceptionally adverse weather as the term is not always defined.
Force majeure clauses need to be flexible enough to cover events which are by their very definition are unforeseeable, but specific enough to prevent disputes arising.
Some forms of construction no longer use the phrase force majeure, but instead include clauses to deal with the specific circumstances that might arise.
In situations where a contractual obligation becomes incapable of being performed, the occurrence might be considered to be a 'frustration event' resulting in termination of the contract. Frustration occurs when circumstances that are not the fault of either party mean it is impossible to continue with the contract. The contract will come to an end without any party being considered to be in breach.
For more information, see Frustration.
NB The Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply (CIPS) Glossary of procurement terms, defines a force majeure as: ‘Circumstances that cannot be foreseen which prevent a contract from being fulfilled.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Breach of contract.
- Clear contracts during uncertain times.
- Compensation event.
- Concurrent delay.
- Consequential loss.
- Coronavirus and force majeure.
- Exculpatory clause.
- Exigency.
- Extension of time.
- Neutral event.
- Frustration.
- Liquidated damages.
- Loss and expense.
- Relevant event.
- Termination.
[edit] External references
- Matsoukis v Priestman & Co (1915).
- Lebeaupin v Crispin (1920).
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
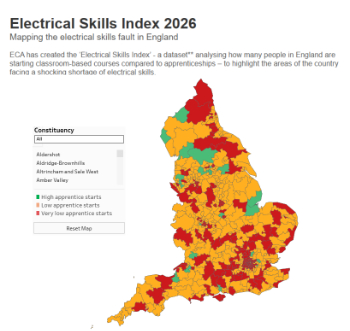
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
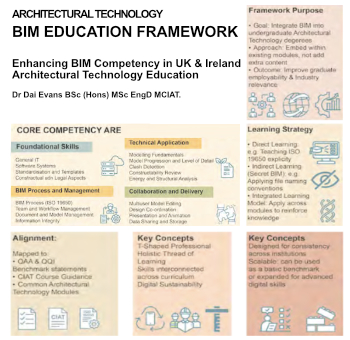
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”